Mobx Counter Example
This is a simple example Counter App made with Mobx, NativeBase and Create React Native App tool. Detailed Setup instructions can be found below.
Find Full Code here
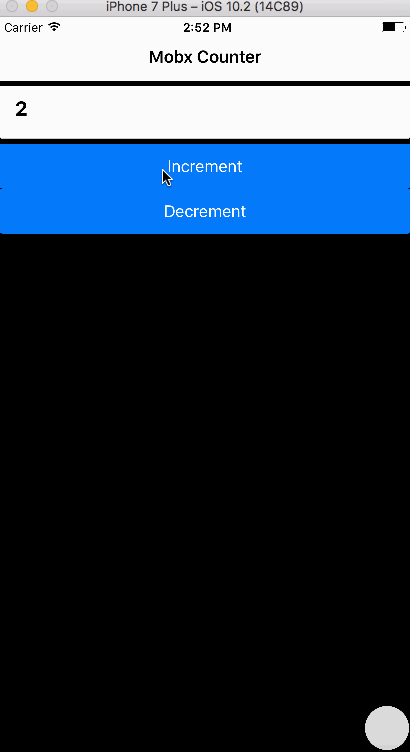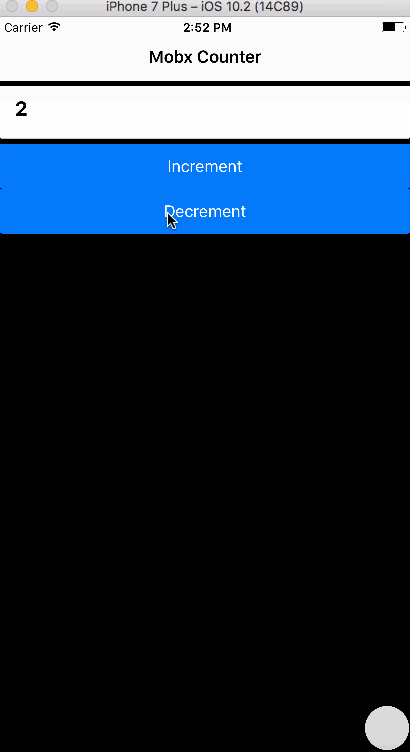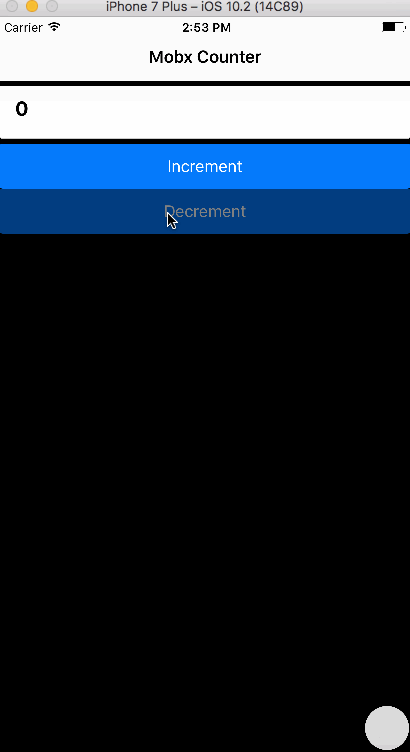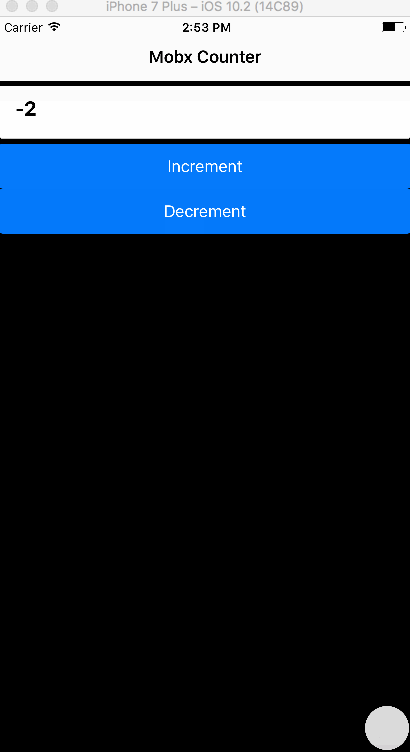
1. Aim
We aim to create a simple App that has a counter with increment and decrement functionality. The logic is implemented in Mobx.
2. Installation
Create React Native App: Use CRNA tool to create an App like this
npm install -g create-react-native-app create-react-native-app my-app cd my-app/ npm startInstall Mobx:
npm i mobx mobx-react --saveInstall babel plugins:
npm i babel-plugin-transform-decorators-legacy babel-preset-react-native-stage-0 --save-dev.babelrc
Now, let’s create a .babelrc file to configure our babel plugins:{ 'presets': ['react-native'], 'plugins': ['transform-decorators-legacy'] }NativeBase
npm install native-base@2 --saveConfigure dependencies
react-native link
Note: Additional steps are required to import fonts from native base. Refer to this
3. Setting Things Up
With all required Libraries installed, we can start with some real coding. In the root of your project create a folder src. Inside this folder we create two files, counterStore.js(The Mobx Store) and counter.js(Counter Component).
By the end of all this your project structure and package.json file should look something like this.
4. Mobx Store Setup
We need to create a Mobx store as follows.
Code src/counterStore.js
import {observable} from 'mobx';
class CounterStore {
@observable counter = 0;
increment() { this.counter++;
console.log("increment", this.counter); }
decrement() { this.counter--;
console.log("decrement", this.counter); }
}
export default new CounterStore();
Explained:
- We import
observablefrommobx. Inside our Store class we create an observable sore variablecounter. - We create two methods
increment()anddecrement()that will be called from out component to update the store. - Lastly, we export a new object of our
storeclass.
5. Mobx Component
We create a counter Component and import it in our main App file.
Code src/conter.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Expo from 'expo';
import { Container, Text, Card, Header, Body, Button, Title, CardItem } from 'native-base';
import CounterStore from './counterStore.js';
import {observer} from 'mobx-react';
import {View} from 'react-native';
@observer
export default class Counter extends Component{
constructor(){
super();
this.state={
isReady: false
}
}
async componentWillMount() {
await Expo.Font.loadAsync({
'Roboto': require('native-base/Fonts/Roboto.ttf'),
'Roboto_medium': require('native-base/Fonts/Roboto_medium.ttf'),
});
this.setState({isReady: true});
}
render(){
if (!this.state.isReady) {
return ;
}
return(
<Container>
<Header>
<Body>
<Title>Mobx Counter</Title>
</Body>
</Header>
<Card>
<CardItem>
<Text>
{CounterStore.counter}
</Text>
</CardItem>
</Card>
<Button primary block onPress= {() => CounterStore.increment()}>
<Text>Increment</Text>
</Button>
<Button primary block onPress= {() => CounterStore.decrement()}>
<Text>Decrement</Text>
</Button>
<View />
</Container>
);
}
}
Explained
- We import
observerfrommobx-reactand make our Classobserverby pre-fixing @observer. async componentWillMount()method is used to load fonts as described here.state.isReadyis used to find out if fonts are loaded. In the meanwhile, we displayExpo.AppLoadingscreen.- We import our
counterStoreand display the observable store valuecounterin aCard. Buttons will fire respective functions from the Store Class.
6. Finishing Up
Lastly we import our counter component in our App.js file.
Build project and run.